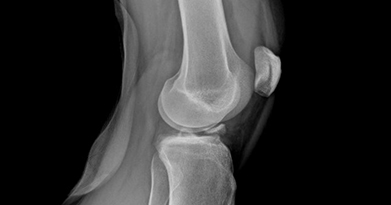
The tibial spine serves as the attachment point for the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It is the also the most prominent aspect within the tibial epiphyseal footprint. The tibial spine may not be fully ossified in children and young adolescents which puts them at risk for avulsion fractures of the tibial spine rather than an ACL rupture because of the partial ossification. Figure 1 shows an xray of a tibial spine avulsion fracture in a younger adult, while Figure 2 shows an xray post reduction and surgical fixation.
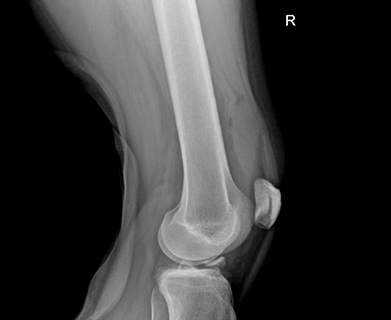
Figure 1
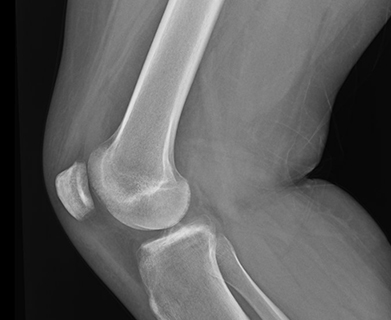
Figure 2
When the tibia is rotated and the knee either hyperextends or is goes into flexion, the force on the ACL avulses or pulls off the tibial spine because it is the weakest point. It is because the tibial spine is the attachment point of the ACL that the mechanism of injury is similar to ACL soft tissue tears in most cases.
The fractures can be classified at Type 1 (minimally displaced), Type 2 (hinged with displacement of the anterior aspect), and Type 3 (completely displaced). Tibial spine fractures can be associated with other injuries including meniscal tears, bone bruising, cartilage injuries, and other non-ACL ligamentous injuries. Plain radiographs can be used to diagnose this injury, but MRI may be needed to identify concomitant injuries to the soft tissue structures. Treatment includes nonoperative management for Type 1 and some Type 2 injuries (reduction within a few millimeters of anatomic to be acceptable). Surgical fixation is indicated for irreducible Type 2 and Type 3 injuries. Surgery is usually performed arthroscopically. Fixation can be accomplished with sutures, suture anchors, or screws. Approach and fixation are often chosen based on fracture characteristics. Figure 3 shows an arthroscopic image of an avulsed tibial spine fracture. Figure 4 shows the ACL tensioned once the tibial spine is reduced while Figure 5 shows the tibial spine fragment reduced and fixed with bioabsorbable screws.
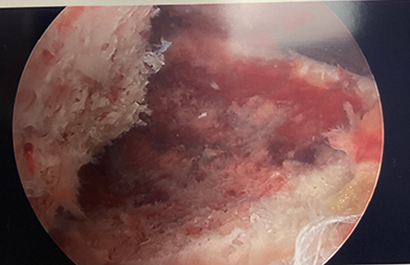
Figure 3
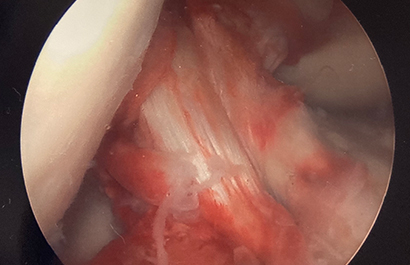
Figure 4
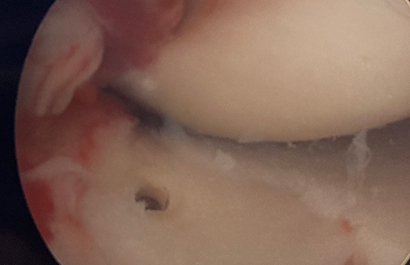
Figure 5
Please contact a board certified sports medicine orthopedic surgeon when seeking treatment regarding a tibial spine avulsion fracture.